Learn: Leben in Deutschland
Question 30
Was ist kein Merkmal unserer Demokratie?
- regelmäßige Wahlen
- Pressezensur
- Meinungsfreiheit
- verschiedene Parteien
Question 30
What is not a characteristic of our democracy?
- regular elections
- press censorship
- freedom of speech
- various parties
The correct answer is 'Pressezensur' (press censorship). In a democracy, regular elections, freedom of speech, and the existence of various political parties are fundamental, while press censorship is contrary to democratic principles.
-
Why is press censorship not a feature of democracy?
Press censorship is not a feature of democracy because democratic systems value transparency and freedom of the press, allowing open discussion and criticism.
-
What are the key features of a democracy?
Key features of a democracy include regular elections, freedom of speech, the presence of various political parties, and the absence of censorship.
-
How does freedom of speech contribute to a democratic society?
Freedom of speech contributes to a democratic society by allowing citizens to express their opinions, debate issues, and hold the government accountable.
- Merkmal: feature
- Demokratie: democracy
- regelmäßige Wahlen: regular elections
- Pressezensur: press censorship
- Meinungsfreiheit: freedom of speech
- verschiedene Parteien: various parties
Question 29
Welches Tier ist das Wappentier der Bundesrepublik Deutschland?
- Löwe
- Adler
- Bär
- Pferd
Question 29
Which animal is the heraldic animal of the Federal Republic of Germany?
- lion
- eagle
- bear
- horse
The correct answer is 'Adler' (eagle). The eagle is the national emblem of the Federal Republic of Germany and is used in various state symbols and official documents.
-
What does the eagle symbolize in the German coat of arms?
The eagle in the German coat of arms symbolizes strength, courage, and independence. It is a traditional symbol of sovereignty and power.
-
When did the eagle become the symbol of the German coat of arms?
The eagle has been the symbol of the German coat of arms since the medieval Holy Roman Empire and continues to be used in modern Germany as a national emblem.
-
Are there other countries that use the eagle as a national symbol?
Yes, many countries use the eagle as a national symbol, including the United States, where it represents freedom and strength, and Mexico, where it is featured on the national flag.
- Wappentier: heraldic animal
- Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Federal Republic of Germany
- Löwe: lion
- Adler: eagle
- Bär: bear
- Pferd: horse
Question 28
Wer wählt in Deutschland die Abgeordneten zum Bundestag?
- das Militär
- die Wirtschaft
- das wahlberechtigte Volk
- die Verwaltung
Question 28
Who elects the members of the Bundestag in Germany?
- the military
- the economy
- the eligible voters
- the administration
The correct answer is 'das wahlberechtigte Volk' (the eligible voters). In Germany, the members of the Bundestag are elected by the eligible voters through general elections.
-
Who can vote in the Bundestag elections?
In Germany, citizens who are at least 18 years old and are eligible to vote can participate in Bundestag elections.
-
How often are Bundestag elections held?
Bundestag elections are held every four years in Germany to elect members of the federal parliament.
-
What is the role of the Bundestag in Germany?
The Bundestag is the federal parliament of Germany, responsible for making national laws, approving the federal budget, and overseeing the executive branch of government.
- Abgeordnete: members of parliament
- Bundestag: federal parliament
- wahlberechtigt: eligible to vote
- Militär: military
- Wirtschaft: economy
- Verwaltung: administration
Question 27
Deutschland ist …
- ein sozialistischer Staat.
- ein Bundesstaat.
- eine Diktatur.
- eine Monarchie.
Question 27
Germany is …
- a socialist state.
- a federal state.
- a dictatorship.
- a monarchy.
Germany is a federal state. This means that it consists of several federal states that together form a unified nation, but also have their own powers and administrative units.
-
What does it mean that Germany is a federal state?
Being a federal state means that Germany is made up of several states that have a certain degree of autonomy but are united under a central government.
-
Which states are part of the federal state of Germany?
Germany is made up of 16 states, including Bavaria, North Rhine-Westphalia, and Berlin.
-
How is a federal state different from a central state?
In a federal state, the member states (like federal states) have certain powers and responsibilities, whereas in a central state, power is predominantly centralized and the regional units have less autonomy.
- sozialistischer Staat: socialist state
- Bundesstaat: federal state
- Diktatur: dictatorship
- Monarchie: monarchy
- Bundesländer: federal states
- Eigenständigkeit: autonomy
Question 26
Deutschland ist …
- eine kommunistische Republik.
- ein demokratischer und sozialer Bundesstaat.
- eine kapitalistische und soziale Monarchie.
- ein sozialer und sozialistischer Bundesstaat.
Question 26
Germany is …
- a communist republic.
- a democratic and social federal state.
- a capitalist and social monarchy.
- a social and socialist federal state.
The correct answer is 'a democratic and social federal state'. Germany is a democratic federal state, which means that there is a system of popular representation through elections and a social market economy that ensures social security and justice.
-
What does it mean when a country is called a 'democratic federal state'?
A democratic federal state is a form of government in which political power is determined by elections and democratic processes and the political units (federal states) have extensive autonomy.
-
What characteristics characterize a 'social market economy'?
A social market economy combines the advantages of the free market with social responsibility. This means that the state intervenes to ensure social justice and security for all citizens.
-
How does a monarchy differ from a republic?
In a monarchy, the government is usually determined by a single person (monarch), while in a republic, power is exercised by elected representatives. In Germany, the form of government is a republic.
- kommunistisch: communist
- Republik: republic
- kapitalistisch: capitalist
- Monarchie: monarchy
- sozialistisch: socialist
- Bundesstaat: federal state
Question 25
Was ist kein Bundesland der Bundesrepublik Deutschland?
- Elsass-Lothringen
- Nordrhein-Westfalen
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Sachsen-Anhalt
Question 25
Which is not a federal state of the Federal Republic of Germany?
- Alsace-Lorraine
- North Rhine-Westphalia
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Saxony-Anhalt
The correct answer is 'Alsace-Lorraine'. Alsace-Lorraine is not one of the current federal states of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was formerly a region that was returned to France after World War I. The other options are valid federal states of Germany.
-
Which federal states belong to the Federal Republic of Germany?
The Federal Republic of Germany includes: Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hesse, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Lower Saxony, North Rhine-Westphalia, Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Schleswig-Holstein and Thuringia.
-
How do the federal states in Germany differ?
The federal states in Germany differ in terms of their size, population, cultural characteristics and political structure. Each federal state has its own government and administration.
-
Why is Alsace-Lorraine not a German federal state?
Alsace-Lorraine is not a current region of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was historically a region that belonged to Germany, but was returned to France after World War I.
- Bundesland: federal state
- Republik: republic
- Land: state
- Bevölkerung: population
- Region: region
- historisch: historically
Question 24
Wie viele Bundesländer hat die Bundesrepublik Deutschland?
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
Question 24
How many federal states does the Federal Republic of Germany have?
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
Germany has a total of 16 federal states. This includes both the original 10 federal states of the Federal Republic of Germany and the 6 new federal states that were added after reunification.
-
How many federal states were there in Germany before reunification?
Before reunification, there were 10 federal states in West Germany and 5 in the former GDR, making a total of 15.
-
Which federal states were added after reunification?
After reunification, five new federal states were added: Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia.
-
What is the political structure of the federal states in Germany?
Each federal state in Germany has its own government and constitution, as well as a certain degree of autonomy in legislation and administration. They are part of the federal system of the Federal Republic of Germany.
- Bundesländer: federal states
- Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Federal Republic of Germany
- Wiedervereinigung: reunification
- politische Struktur: political structure
- Autonomie: autonomy
Question 23
In Deutschland sind die meisten Erwerbstätigen …
- in kleinen Familienunternehmen beschäftigt.
- ehrenamtlich für ein Bundesland tätig.
- selbstständig mit einer eigenen Firma tätig.
- bei einer Firma oder Behörde beschäftigt.
Question 23
In Germany, most employed people are …
- employed in small family businesses.
- voluntarily working for a federal state.
- self-employed with their own company.
- employed by a company or authority.
The majority of employed people in Germany are employed by a company or public authority. This includes a wide range of jobs in various sectors of the economy and public service.
-
What percentage of the working population in Germany is employed by companies or public authorities?
In Germany, about 80% of the working population is employed by companies or public authorities, while the rest are self-employed or work in small family-owned businesses.
-
What is the significance of small family-owned businesses in Germany?
Small family-owned businesses play an important role in the German economy, as they create a significant portion of jobs and often offer innovative products and services.
-
What are the most common sectors in which the majority of the working population in Germany is employed?
The most common sectors are services, trade, healthcare, and industry. Many workers are employed in companies or public authorities in these sectors.
- Erwerbstätige: employees
- Familienunternehmen: family businesses
- ehrenamtlich: voluntarily
- selbstständig: self-employed
- Behörde: authority
Question 22
Was für eine Staatsform hat Deutschland?
- Monarchie
- Diktatur
- Republik
- Fürstentum
Question 22
What form of government does Germany have?
- Monarchy
- Dictatorship
- Republic
- Principality
Germany is a republic. This means that the head of state is not determined by hereditary succession, but is usually elected. Germany is not a monarchy, dictatorship or principality.
-
What is the difference between a republic and a monarchy?
In a republic, the head of state is usually elected and often has a term limited by time. In a monarchy, the head of state is determined by heredity and often has a lifelong tenure.
-
What form of government does Germany have today?
Germany is a federal republic, more precisely a democratic republic, in which the form of government is regulated by the Basic Law.
-
How does the form of government influence the government in Germany?
As a republic, Germany has a system of popular representation and the election of representatives. This means that citizens influence the government and policy through elections.
- Staatsform: form of government
- Monarchie: monarchy
- Diktatur: dictatorship
- Republik: republic
- Fürstentum: principality
Question 21
Welches ist das Wappen der Bundesrepublik Deutschland?
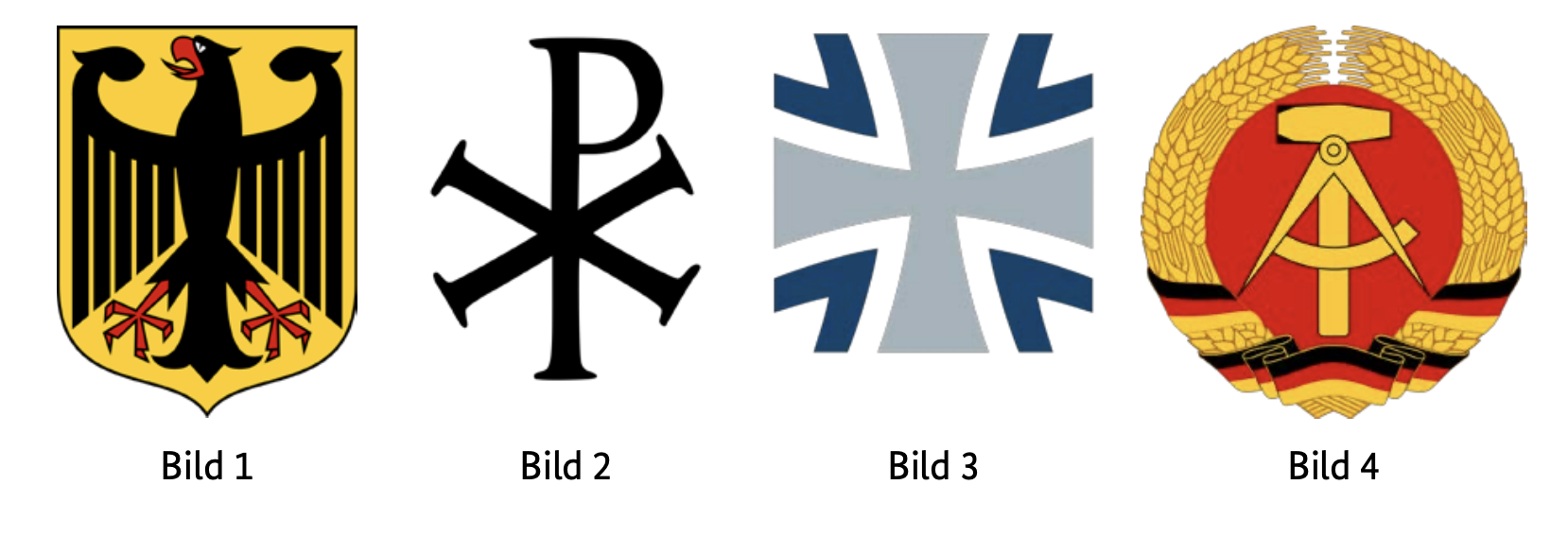
- Bild 1
- Bild 2
- Bild 3
- Bild 4
Question 21
Which is the coat of arms of the Federal Republic of Germany?

- Image 1
- Image 2
- Image 3
- Image 4
The correct coat of arms of the Federal Republic of Germany is 'Image 1'. It shows a black eagle on a golden background, which has been used as a heraldic animal since the founding of the Federal Republic of Germany.
-
What does the coat of arms of the Federal Republic of Germany show?
The coat of arms of the Federal Republic of Germany shows a black eagle on a golden background.
-
Why is the eagle the heraldic animal of Germany?
The eagle is used as a symbol of strength and independence and has a long tradition as a heraldic animal in Germany.
-
When was the current coat of arms of Germany introduced?
The current coat of arms of Germany was introduced after World War II and has been in use in the Federal Republic of Germany since 1949.
- Wappen: coat of arms
- Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Federal Republic of Germany
- Adler: eagle
- Hintergrund: background
- schwarz: black
- golden: golden
Question 20
Eine Partei in Deutschland verfolgt das Ziel, eine Diktatur zu errichten. Sie ist dann …
- tolerant.
- rechtsstaatlich orientiert.
- gesetzestreu.
- verfassungswidrig.
Question 20
A party in Germany that aims to establish a dictatorship is then ...
- tolerant.
- oriented towards the rule of law.
- law-abiding.
- unconstitutional.
The correct answer is 'verfassungswidrig' (unconstitutional). In Germany, a political party that seeks to establish a dictatorship is considered unconstitutional because it aims to overthrow or undermine the democratic principles established by the constitution.
-
What does 'unconstitutional' mean in the context of political parties?
'Unconstitutional' refers to actions or goals that are in violation of a country's constitution. In the context of political parties, it means pursuing objectives that undermine the democratic framework of the state.
-
Why is a party aiming to establish a dictatorship considered unconstitutional?
A party aiming to establish a dictatorship seeks to dismantle democratic institutions and processes, which directly contravenes the principles enshrined in a democratic constitution.
-
What are the consequences for a party found to be unconstitutional in Germany?
Such a party can be banned by the Federal Constitutional Court if it is deemed to threaten the democratic order. This is to protect the democratic and constitutional integrity of the country.
- Diktatur: dictatorship
- verfassungswidrig: unconstitutional
- rechtsstaatlich orientiert: oriented towards the rule of law
- gesetzestreu: law-abiding
- tolerant: tolerant
Question 19
Was versteht man unter dem Recht der "Freizügigkeit" in Deutschland?
- Man darf sich seinen Wohnort selbst aussuchen.
- Man kann seinen Beruf wechseln.
- Man darf sich für eine andere Religion entscheiden.
- Man darf sich in der Öffentlichkeit nur leicht bekleidet bewegen.
Question 19
What is meant by the right of 'freedom of movement' in Germany?
- One is allowed to choose one's place of residence.
- One can change their profession.
- One can choose a different religion.
- One may only dress lightly in public.
The correct answer is 'Man darf sich seinen Wohnort selbst aussuchen.' (One is allowed to choose one's place of residence). In Germany, the right of 'freedom of movement' means that individuals can select their place of residence and move freely within the country.
-
What is meant by the right of 'freedom of movement' in Germany?
The right of 'freedom of movement' in Germany refers to the ability of individuals to choose their place of residence and move freely within the country.
-
How does the right of freedom of movement impact German citizens?
This right allows German citizens to live in any part of the country they choose, facilitating greater personal freedom and flexibility in their lives.
-
Are there any restrictions on the freedom of movement in Germany?
Generally, there are no restrictions on the freedom of movement within Germany, but there may be specific regulations or requirements in exceptional cases, such as for public health reasons.
- Freizügigkeit: freedom of movement
- Wohnort: place of residence
- Beruf: profession
- Religion: religion
- Öffentlichkeit: public
Question 18
Welches Grundrecht ist in Artikel 1 des Grundgesetzes der Bundesrepublik Deutschland garantiert?
- die Unantastbarkeit der Menschenwürde
- das Recht auf Leben
- Religionsfreiheit
- Meinungsfreiheit
Question 18
Which fundamental right is guaranteed in Article 1 of the Basic Law of the Federal Republic of Germany?
- the inviolability of human dignity
- the right to life
- freedom of religion
- freedom of opinion
The correct answer is 'die Unantastbarkeit der Menschenwürde' (the inviolability of human dignity). Article 1 of the Basic Law of Germany guarantees the inviolability of human dignity as a fundamental right, making it the highest value in German constitutional law.
-
What fundamental right is guaranteed in Article 1 of the Basic Law of the Federal Republic of Germany?
Article 1 of the Basic Law guarantees the inviolability of human dignity as a fundamental right.
-
Why is the inviolability of human dignity important in Germany's constitution?
The inviolability of human dignity is crucial because it forms the cornerstone of the German constitution, emphasizing the respect and protection of every individual's dignity.
-
How does the German constitution protect human dignity?
The German constitution protects human dignity by ensuring that all governmental actions and laws must respect and uphold the inherent worth of every individual.
- Grundrecht: fundamental right
- Unantastbarkeit: inviolability
- Menschenwürde: human dignity
- Artikel: Article
- Grundgesetz: Basic Law
Question 17
Die deutschen Gesetze verbieten …
- Meinungsfreiheit der Einwohnerinnen und Einwohner.
- Petitionen der Bürgerinnen und Bürger.
- Versammlungsfreiheit der Einwohnerinnen und Einwohner.
- Ungleichbehandlung der Bürgerinnen und Bürger durch den Staat.
Question 17
German laws prohibit …
- freedom of opinion for residents
- petitions by citizens
- freedom of assembly for residents
- discrimination of citizens by the state
The correct answer is 'Ungleichbehandlung der Bürgerinnen und Bürger durch den Staat' (discrimination of citizens by the state). German laws prohibit the state from discriminating against citizens, thus ensuring equality and fairness.
-
What do German laws prohibit in terms of treatment by the state?
German laws prohibit the discrimination of citizens by the state, ensuring equal treatment for all.
-
What rights are protected under German law?
German law protects fundamental rights such as freedom of opinion, freedom of assembly, and the right to petition.
-
How does German law ensure equality among citizens?
German law ensures equality by forbidding any form of discrimination by the state and upholding the principle of equal treatment for all citizens.
- Gesetze: laws
- Meinungsfreiheit: freedom of opinion
- Petitionen: petitions
- Versammlungsfreiheit: freedom of assembly
- Ungleichbehandlung: discrimination
Question 16
Wann ist die Meinungsfreiheit in Deutschland eingeschränkt?
- bei der öffentlichen Verbreitung falscher Behauptungen über einzelne Personen
- bei Meinungsäußerungen über die Bundesregierung
- bei Diskussionen über Religionen
- bei Kritik am Staat
Question 16
When is freedom of speech restricted in Germany?
- in the public dissemination of false claims about individuals
- in statements about the federal government
- in discussions about religions
- in criticism of the state
The correct answer is 'bei der öffentlichen Verbreitung falscher Behauptungen über Einzelne' (in the public dissemination of false claims about individuals). In Germany, freedom of speech is restricted to prevent defamation and protect individuals' reputations.
-
When is freedom of speech restricted in Germany?
Freedom of speech in Germany is restricted in cases of public dissemination of false claims about individuals, to protect personal reputation and prevent defamation.
-
What are some examples of restricted freedom of speech in Germany?
Examples include the spread of false information that could harm someone's reputation, incitement to violence, and hate speech.
-
Can you criticize the government in Germany?
Yes, criticizing the government is allowed in Germany. However, freedom of speech does not extend to spreading false claims or inciting violence.
- Meinungsfreiheit: freedom of speech
- öffentliche Verbreitung: public dissemination
- falsche Behauptungen: false claims
- Einzelne: individuals
- eingeschränkt: restricted