Learn: Leben in Deutschland
Question 210
Was ereignete sich am 17. Juni 1953 in der DDR?
- der feierliche Beitritt zum Warschauer Pakt
- landesweite Streiks und ein Volksaufstand
- der 1. SED-Parteitag
- der erste Besuch Fidel Castros
Question 210
What happened on June 17, 1953, in the DDR?
- the ceremonial accession to the Warsaw Pact
- nationwide strikes and a popular uprising
- the 1st SED Party Congress
- the first visit of Fidel Castro
The correct answer is 'landesweite Streiks und ein Volksaufstand' (nationwide strikes and a popular uprising). On June 17, 1953, East Germany experienced a series of protests and strikes against the communist government, which were brutally suppressed by Soviet forces.
-
What happened on June 17, 1953, in the DDR?
On June 17, 1953, there were nationwide strikes and a popular uprising against the government in East Germany (DDR).
-
What caused the uprising on June 17, 1953, in East Germany?
The uprising was sparked by workers' demands for better living conditions and political freedoms, leading to widespread protests and strikes.
-
How did the DDR government respond to the uprising on June 17, 1953?
The DDR government, with the help of Soviet troops, violently suppressed the uprising, resulting in numerous deaths and arrests.
-
Why is June 17, 1953, significant in German history?
June 17, 1953, is significant as it represents the first major uprising against the communist regime in East Germany, symbolizing the people's resistance to oppressive rule.
- Streiks: strikes
- Volksaufstand: popular uprising
- ereignete sich: occurred
Question 209
Welches war das Wappen der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik?
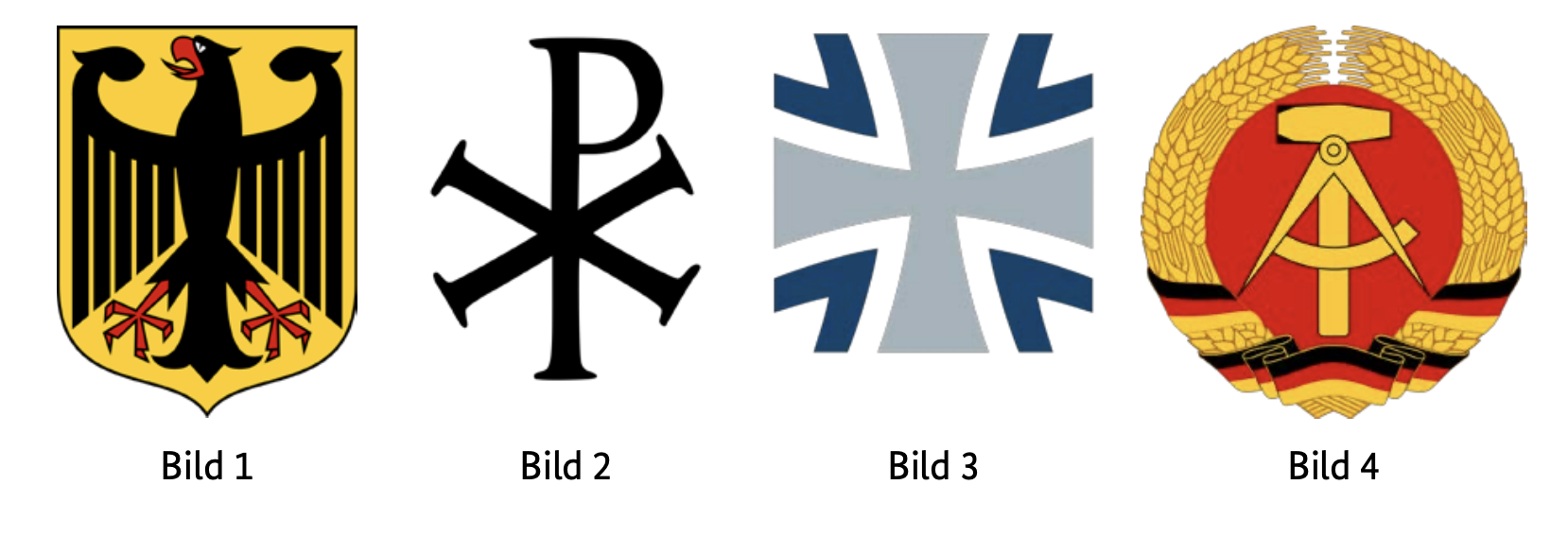
- Bild 1
- Bild 2
- Bild 3
- Bild 4
Question 209
Which was the coat of arms of the German Democratic Republic?

- Image 1
- Image 2
- Image 3
- Image 4
The correct answer is 'Bild 4' (Image 4). The coat of arms of the Deutsche Demokratische Republik (DDR) included a hammer, compass, and a wreath of grain, symbolizing the alliance between workers, peasants, and intellectuals.
-
What did the coat of arms of the DDR (East Germany) look like?
The coat of arms of the DDR featured a hammer and a compass surrounded by a wreath of grain, symbolizing the working class, intellectual labor, and agriculture.
-
What did the symbols on the DDR coat of arms represent?
The hammer represented the working class, the compass stood for the intelligentsia, and the wreath of grain symbolized the farmers and agricultural workers.
-
How was the DDR coat of arms used?
The DDR coat of arms was used as the official emblem of East Germany, appearing on government buildings, official documents, and the national flag.
- Wappen: coat of arms
- Deutsche Demokratische Republik (DDR): German Democratic Republic (DDR)
- Hammer: hammer
- Zirkel: compass
- Ährenkranz: wreath of grain
Question 208
Was war die "Stasi"?
- der Geheimdienst im "Dritten Reich"
- eine berühmte deutsche Gedenkstätte
- der Geheimdienst der DDR
- ein deutscher Sportverein während des Zweiten Weltkrieges
Question 208
What was the 'Stasi'?
- the secret service in the 'Third Reich'
- a famous German memorial site
- the secret service of the DDR
- a German sports club during World War II
The correct answer is 'der Geheimdienst der DDR' (the secret service of the DDR). The Stasi was the official state security service of East Germany (DDR) and was known for its extensive surveillance and suppression of dissent.
-
What was the Stasi?
The Stasi was the official state security service of the German Democratic Republic (DDR), responsible for surveillance, espionage, and maintaining control over the population.
-
How did the Stasi operate in East Germany?
The Stasi used extensive surveillance, wiretapping, and informants to monitor and suppress dissent in East Germany. They maintained files on millions of citizens.
-
What was the role of the Stasi during the Cold War?
During the Cold War, the Stasi acted as the DDR's secret police and espionage agency, collaborating closely with the KGB to suppress internal dissent and spy on Western nations.
-
When did the Stasi dissolve?
The Stasi was dissolved in 1990 after the fall of the Berlin Wall and the subsequent reunification of Germany.
- Stasi: Stasi (abbreviation for Staatssicherheit)
- Geheimdienst: secret service
- DDR: German Democratic Republic (East Germany)
Question 207
In welchem Militärbündnis war die DDR Mitglied?
- in der NATO
- im Rheinbund
- im Warschauer Pakt
- im Europabündnis
Question 207
In which military alliance was the DDR a member?
- in NATO
- in the Confederation of the Rhine
- in the Warsaw Pact
- in the European Alliance
The correct answer is 'im Warschauer Pakt' (in the Warsaw Pact). The DDR (East Germany) was a member of the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance of communist countries during the Cold War, led by the Soviet Union.
-
What was the Warsaw Pact?
The Warsaw Pact was a military alliance of communist countries in Eastern Europe, led by the Soviet Union, established as a counterbalance to NATO during the Cold War.
-
Was the DDR part of NATO?
No, the DDR (East Germany) was part of the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance of Eastern Bloc countries, while West Germany was a member of NATO.
-
When did the Warsaw Pact exist?
The Warsaw Pact was established in 1955 and lasted until 1991, when it dissolved following the end of the Cold War.
-
What was the role of the DDR in the Warsaw Pact?
The DDR (East Germany) was a key member of the Warsaw Pact, hosting Soviet military forces and contributing to the military efforts of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War.
- Militärbündnis: military alliance
- Warschauer Pakt: Warsaw Pact
- DDR: German Democratic Republic
Question 206
Woran erinnern die sogenannten „Stolpersteine“ in Deutschland?
- an berühmte deutsche Politikerinnen und Politiker
- an die Opfer des Nationalsozialismus
- an Verkehrstote
- an bekannte jüdische Musiker
Question 206
What do the so-called 'Stolpersteine' in Germany commemorate?
- to famous German politicians
- to the victims of National Socialism
- to traffic accident victims
- to well-known Jewish musicians
The correct answer is 'an die Opfer des Nationalsozialismus' (to the victims of National Socialism). Stolpersteine are small brass plaques embedded in sidewalks, commemorating individuals persecuted or murdered by the Nazis during the Holocaust.
-
What are Stolpersteine?
Stolpersteine are small brass plaques embedded in sidewalks throughout Germany and Europe. They commemorate individuals who were persecuted or murdered by the Nazis, especially Jews, Roma, political dissidents, and others.
-
Where can Stolpersteine be found?
Stolpersteine can be found outside the last known residences or workplaces of victims of National Socialism. They serve as a poignant reminder of the individuals who once lived in these places.
-
Who initiated the Stolpersteine project?
The Stolpersteine project was initiated by German artist Gunter Demnig in the 1990s as a decentralized, grassroots way to remember the victims of the Holocaust.
-
Why are they called Stolpersteine (stumbling stones)?
They are called Stolpersteine because, metaphorically, they cause passersby to 'stumble' upon the memory of the victims. The stones invite people to pause and reflect on the atrocities of the past.
- Stolpersteine: stumbling stones
- Opfer: victims
- Nationalsozialismus: National Socialism
Question 205
Mit dem Beitritt der DDR zur Bundesrepublik Deutschland gehören die neuen Bundesländer nun auch …
- zur Europäischen Union.
- zum Warschauer Pakt.
- zur OPEC.
- zur Europäischen Verteidigungsgemeinschaft.
Question 205
With the accession of the DDR to the Federal Republic of Germany, the new federal states also belong to …
- to the European Union.
- to the Warsaw Pact.
- to OPEC.
- to the European Defense Community.
The correct answer is 'zur Europäischen Union' (to the European Union). When the DDR joined the Federal Republic of Germany in 1990, the new federal states also became part of the European Union.
-
What happened when the DDR joined the Federal Republic of Germany?
When the DDR (East Germany) joined the Federal Republic of Germany in 1990, the new federal states automatically became part of the European Union as well.
-
Did the new federal states join the Warsaw Pact after reunification?
No, the Warsaw Pact was a military alliance for Eastern Bloc countries. After reunification, the new federal states became part of the European Union and NATO, as they were integrated into the Federal Republic of Germany.
-
What is OPEC, and is Germany a member?
OPEC is the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries. Germany is not a member of OPEC.
-
How did reunification affect Germany's role in Europe?
Reunification expanded the Federal Republic of Germany's presence in the European Union by adding the new federal states from the former East Germany.
- Beitritt: accession
- Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Federal Republic of Germany
- Europäische Union: European Union
Question 204
Wie wurden die Bundesrepublik Deutschland und die DDR zu einem Staat?
- Die Bundesrepublik hat die DDR besetzt.
- Die heutigen fünf östlichen Bundesländer sind der Bundesrepublik Deutschland beigetreten.
- Die westlichen Bundesländer sind der DDR beigetreten.
- Die DDR hat die Bundesrepublik Deutschland besetzt.
Question 204
How did the Federal Republic of Germany and the DDR become one state?
- The Federal Republic occupied the DDR.
- The current five eastern federal states joined the Federal Republic.
- The western federal states joined the DDR.
- The DDR occupied the Federal Republic of Germany.
The correct answer is 'Die heutigen fünf östlichen Bundesländer sind der Bundesrepublik beigetreten.' (The current five eastern federal states joined the Federal Republic). This reflects the peaceful reunification of East and West Germany in 1990.
-
How did the reunification of Germany happen?
Reunification occurred when the five eastern states of the former DDR joined the Federal Republic of Germany in 1990, creating a unified state.
-
Did the Federal Republic occupy the DDR?
No, reunification happened through peaceful negotiations, and the DDR's five eastern federal states joined the Federal Republic of Germany.
-
What were the five eastern federal states that joined the Federal Republic?
The five eastern federal states are Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia.
-
Was the reunification of Germany a forced occupation?
No, reunification was a peaceful process involving negotiations between East and West Germany, leading to the integration of the DDR into the Federal Republic.
- Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Federal Republic of Germany
- besetzt: occupied
- beigetreten: joined
Question 203
Wie hieß das Wirtschaftssystem der DDR?
- Marktwirtschaft
- Planwirtschaft
- Angebot und Nachfrage
- Kapitalismus
Question 203
What was the economic system of the DDR called?
- market economy
- planned economy
- supply and demand
- capitalism
The correct answer is 'Planwirtschaft' (planned economy). The DDR had a centrally planned economy where the state controlled all aspects of economic production and distribution.
-
What was the economic system of the DDR?
The economic system of the DDR was a 'Planwirtschaft' (planned economy), where the government controlled production, prices, and distribution of goods.
-
How does a planned economy differ from a market economy?
In a planned economy, the government makes all economic decisions, while in a market economy, these decisions are driven by supply and demand forces.
-
Why did the DDR use a planned economy?
The DDR, as a socialist state, adopted a planned economy to centralize economic control and implement socialist principles.
-
What were the challenges of the planned economy in the DDR?
The planned economy of the DDR faced inefficiencies, shortages of goods, and low productivity due to rigid government control and lack of competition.
- Planwirtschaft: planned economy
- Marktwirtschaft: market economy
- Kapitalismus: capitalism
Question 202
Zu wem gehörte die DDR im 'Kalten Krieg'?
- zu den Westmächten
- zum Warschauer Pakt
- zur NATO
- zu den blockfreien Staaten
Question 202
To which alliance did the DDR belong during the Cold War?
- to the Western powers
- to the Warsaw Pact
- to NATO
- to the non-aligned states
The correct answer is 'zum Warschauer Pakt' (to the Warsaw Pact). The DDR (East Germany) was a member of the Warsaw Pact, which was a military alliance of communist countries led by the Soviet Union during the Cold War.
-
What was the Warsaw Pact?
The Warsaw Pact was a military alliance of communist countries in Eastern Europe, led by the Soviet Union, formed as a counterpart to NATO during the Cold War.
-
Which side of the Cold War did the DDR belong to?
The DDR (East Germany) was aligned with the Soviet Union and was a member of the Warsaw Pact during the Cold War.
-
Was the DDR part of NATO?
No, the DDR was part of the Warsaw Pact, which opposed NATO during the Cold War. West Germany, however, was a member of NATO.
-
What were the non-aligned states?
The non-aligned states were countries that did not formally align themselves with either the Western powers (NATO) or the Eastern Bloc (Warsaw Pact) during the Cold War.
- Kalter Krieg: Cold War
- Warschauer Pakt: Warsaw Pact
- Westmächte: Western powers
- blockfreie Staaten: non-aligned states
Question 201
Welche der folgenden Auflistungen enthält nur Bundesländer, die zum Gebiet der früheren DDR gehörten?
- Niedersachsen, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Hessen, Schleswig-Holstein, Brandenburg
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Sachsen, Sachsen-Anhalt, Thüringen
- Bayern, Baden-Württemberg, Rheinland-Pfalz, Thüringen, Sachsen
- Sachsen, Thüringen, Hessen, Niedersachsen, Brandenburg
Question 201
Which of the following lists contains only federal states that were part of the former DDR?
- Lower Saxony, North Rhine-Westphalia, Hesse, Schleswig-Holstein, Brandenburg
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Thüringen
- Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg, Rhineland-Palatinate, Thuringia, Saxony
- Saxony, Thuringia, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Brandenburg
The correct answer is 'Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Sachsen, Sachsen-Anhalt.' These states were part of the former DDR before German reunification in 1990.
-
Which federal states were part of the former DDR?
The states that were part of the former DDR are Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia.
-
Was Saxony a part of the DDR?
Yes, Saxony was part of the former DDR.
-
Are states like Bavaria and Hesse part of the former DDR?
No, Bavaria and Hesse were part of West Germany and were not included in the territory of the former DDR.
-
What happened to the federal states after reunification?
After reunification, the five new federal states of the former DDR were integrated into the Federal Republic of Germany, creating a unified country.
- Bundesländer: federal states
- frühere DDR: former German Democratic Republic (DDR)
Question 200
Welches heutige deutsche Bundesland gehörte früher zum Gebiet der DDR?
- Hessen
- Schleswig-Holstein
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Saarland
Question 200
Which modern German federal state was previously part of the DDR?
- Hesse
- Schleswig-Holstein
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Saarland
The correct answer is 'Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.' This state was part of the DDR (East Germany) before reunification in 1990 and is now one of Germany's 16 federal states.
-
Which modern federal state was part of the former DDR?
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern was part of the former DDR before German reunification.
-
Was Hesse ever part of the DDR?
No, Hesse was part of West Germany and was never part of the DDR.
-
What happened to the states that were part of the DDR after reunification?
After reunification, the former DDR states, including Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, became part of the unified Federal Republic of Germany.
-
Was Mecklenburg-Vorpommern affected by the reunification of Germany?
Yes, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern became one of the new federal states of the unified Germany after the DDR joined the Federal Republic in 1990.
- heutige: modern/current
- Bundesland: federal state
- DDR: German Democratic Republic (East Germany)
Question 199
Mit der Abkürzung "Stasi" meinte man in der DDR …
- das Parlament.
- das Ministerium für Staatssicherheit.
- eine regierende Partei.
- das Ministerium für Volksbildung.
Question 199
The abbreviation 'Stasi' in the DDR referred to …
- the parliament.
- the Ministry for State Security.
- a ruling party.
- the Ministry for People's Education.
The correct answer is 'das Ministerium für Staatssicherheit' (the Ministry for State Security). The Stasi was the state security service in the DDR, responsible for surveillance, intelligence, and suppressing opposition.
-
What did the abbreviation 'Stasi' stand for?
The abbreviation 'Stasi' referred to the 'Ministerium für Staatssicherheit,' which was the state security service of the DDR.
-
What was the role of the Stasi in East Germany?
The Stasi was responsible for internal security, surveillance, and intelligence in the DDR. It monitored citizens, suppressed dissent, and maintained control over the population.
-
How did the Stasi impact the daily lives of DDR citizens?
The Stasi infiltrated almost every aspect of life in the DDR, using a vast network of informants to spy on ordinary citizens, leading to a culture of fear and distrust.
-
When did the Stasi dissolve?
The Stasi was dissolved in 1990 following the fall of the Berlin Wall and the reunification of Germany.
- Abkürzung: abbreviation
- Stasi: Stasi (Ministry for State Security)
- Ministerium für Staatssicherheit: Ministry for State Security
- DDR: German Democratic Republic (East Germany)
Question 198
Welches heutige deutsche Bundesland gehörte früher zum Gebiet der DDR?
- Bayern
- Niedersachsen
- Sachsen
- Baden-Württemberg
Question 198
Which modern German federal state was previously part of the DDR?
- Bavaria
- Lower Saxony
- Saxony
- Baden-Württemberg
The correct answer is 'Sachsen' (Saxony). Saxony was part of the former DDR before reunification in 1990 and is now one of Germany's 16 federal states.
-
Which modern German state was part of the former DDR?
Saxony (Sachsen) was part of the former DDR before reunification.
-
Was Bavaria (Bayern) part of the DDR?
No, Bavaria was part of West Germany and was not included in the territory of the former DDR.
-
What happened to Saxony after German reunification?
After reunification in 1990, Saxony became one of the federal states of unified Germany.
-
Did any western German states belong to the DDR?
No, only eastern states like Saxony were part of the DDR. Western states such as Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg were part of West Germany.
- heutige: modern/current
- Bundesland: federal state
- DDR: German Democratic Republic (East Germany)
Question 197
Welches heutige deutsche Bundesland gehörte früher zum Gebiet der DDR?
- Thüringen
- Hessen
- Bayern
- Bremen
Question 197
Which modern German federal state was previously part of the DDR?
- Thuringia
- Hesse
- Bavaria
- Bremen
The correct answer is 'Thüringen' (Thuringia). Thuringia was part of the former DDR before reunification in 1990 and is now one of Germany's 16 federal states.
-
Which modern German state was part of the former DDR?
Thuringia (Thüringen) was part of the former DDR before reunification.
-
Was Hesse (Hessen) part of the DDR?
No, Hesse was part of West Germany and was not included in the territory of the former DDR.
-
What happened to Thuringia after German reunification?
After reunification in 1990, Thuringia became one of the federal states of unified Germany.
-
Did any western German states belong to the DDR?
No, only eastern states like Thuringia were part of the DDR. Western states such as Hesse and Bavaria were part of West Germany.
- heutige: modern/current
- Bundesland: federal state
- DDR: German Democratic Republic (East Germany)
Question 196
Warum nennt man die Zeit im Herbst 1989 in der DDR "Die Wende"? In dieser Zeit veränderte sich die DDR politisch …
- von einer Diktatur zur Demokratie.
- von einer liberalen Marktwirtschaft zum Sozialismus.
- von einer Monarchie zur Sozialdemokratie.
- von einem religiösen Staat zu einem kommunistischen Staat.
Question 196
Why is the period in autumn 1989 in the DDR called 'Die Wende'? During this time, the DDR changed politically ...
- from a dictatorship to a democracy.
- from a liberal market economy to socialism.
- from a monarchy to social democracy.
- from a religious state to a communist state.
The correct answer is 'von einer Diktatur zur Demokratie' (from a dictatorship to a democracy). 'Die Wende' refers to the political transformation that took place in East Germany (DDR) in 1989, resulting in the end of communist rule and the eventual reunification of Germany.
-
What was 'Die Wende' in 1989?
'Die Wende' refers to the political transformation in East Germany (DDR) in 1989, which marked the transition from a dictatorship to a democracy, ultimately leading to the fall of the Berlin Wall and reunification.
-
Why is 'Die Wende' important in German history?
'Die Wende' represents a crucial period in German history that led to the end of communist rule in East Germany and paved the way for German reunification in 1990.
-
How did 'Die Wende' affect East Germany?
During 'Die Wende,' East Germany experienced widespread protests, political reforms, and the eventual collapse of the communist regime, leading to democratic elections and reunification with West Germany.
-
What was the role of the Berlin Wall in 'Die Wende'?
The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, was a pivotal moment during 'Die Wende,' symbolizing the end of division and the beginning of the reunification process.
- Die Wende: the turning point
- Diktatur: dictatorship
- Demokratie: democracy