Learn: Leben in Deutschland
Question 180
Der erste Bundeskanzler der Bundesrepublik Deutschland war …
- Ludwig Erhard.
- Willy Brandt.
- Konrad Adenauer.
- Gerhard Schröder.
Question 180
The first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany was …
- Ludwig Erhard.
- Willy Brandt.
- Konrad Adenauer.
- Gerhard Schröder.
The correct answer is 'Konrad Adenauer.' Konrad Adenauer was the first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany, serving from 1949 to 1963. He played a key role in Germany's post-war recovery and integration into the Western world.
-
Who was the first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany?
The first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany was Konrad Adenauer, who served from 1949 to 1963.
-
What was Konrad Adenauer known for?
Konrad Adenauer is known for his role in rebuilding West Germany after World War II and his leadership in the establishment of the European Economic Community (EEC), a precursor to the European Union.
-
Why was Konrad Adenauer significant in post-war Germany?
Adenauer was significant for promoting West Germany's integration into the Western world, fostering economic recovery, and establishing strong ties with the United States and Western Europe.
-
How long did Konrad Adenauer serve as Chancellor?
Konrad Adenauer served as Chancellor for 14 years, from 1949 to 1963, making him one of Germany's longest-serving leaders.
-
What was Konrad Adenauer's political party?
Konrad Adenauer was a member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), which he helped to found after World War II.
- Bundeskanzler: Chancellor
- Bundesrepublik: Federal Republic
Question 179
Wie endete der Zweite Weltkrieg in Europa offiziell?
- mit dem Tod Adolf Hitlers
- durch die bedingungslose Kapitulation Deutschlands
- mit dem Rückzug der Deutschen aus den besetzten Gebieten
- durch eine Revolution in Deutschland
Question 179
How did World War II officially end in Europe?
- with the death of Adolf Hitler
- through Germany's unconditional surrender
- with the withdrawal of the Germans from the occupied territories
- through a revolution in Germany
The correct answer is 'durch die bedingungslose Kapitulation Deutschlands' (through Germany's unconditional surrender). World War II in Europe officially ended on May 8, 1945, with Germany's unconditional surrender to the Allied forces.
-
How did World War II officially end in Europe?
World War II officially ended in Europe with Germany's unconditional surrender on May 8, 1945.
-
Why did Germany surrender in 1945?
Germany surrendered after being defeated by the Allied forces, with the collapse of Nazi leadership following Adolf Hitler's suicide.
-
What was the significance of May 8, 1945?
May 8, 1945, is known as Victory in Europe (V-E) Day, marking the official end of World War II in Europe.
-
Who accepted Germany's surrender?
Germany's unconditional surrender was accepted by the Allied forces, represented by the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom.
-
What happened to Germany after the war?
After the war, Germany was divided into occupation zones controlled by the Allied powers, leading to the eventual division into East and West Germany during the Cold War.
- endete: ended
- Zweite Weltkrieg: Second World War
- offiziell: officially
- Tod: death
- Kapitulation: surrender
- bedingungslos: unconditional
- Rückzug: withdrawal
- besetzten Gebieten: occupied territories
- Revolution: revolution
Question 178
Vom Juni 1948 bis zum Mai 1949 wurden die Bürgerinnen und Bürger von West-Berlin durch eine Luftbrücke versorgt. Welcher Umstand war dafür verantwortlich?
- Für Frankreich war eine Versorgung der West-Berliner Bevölkerung mit dem Flugzeug kostengünstiger.
- Die amerikanischen Soldatinnen und Soldaten hatten beim Landtransport Angst vor Überfällen.
- Für Großbritannien war die Versorgung über die Luftbrücke schneller.
- Die Sowjetunion unterbrach den gesamten Verkehr auf dem Landwege.
Question 178
From June 1948 to May 1949, the citizens of West Berlin were supplied by an airlift. What was the reason for this?
- For France, supplying the West Berlin population by plane was more cost-effective.
- The American soldiers were afraid of being attacked during land transport.
- For Great Britain, the supply via airlift was faster.
- The Soviet Union blocked all land routes.
The correct answer is 'Die Sowjetunion unterbrach den gesamten Verkehr auf dem Landwege.' (The Soviet Union blocked all land routes). The Berlin Airlift was a response to the Soviet blockade of land and rail routes to West Berlin from June 1948 to May 1949.
-
What was the Berlin Airlift?
The Berlin Airlift (Luftbrücke) was an operation from June 1948 to May 1949 in which Western Allies supplied West Berlin by air after the Soviet Union blocked all land and rail routes to the city.
-
Why did the Soviet Union block West Berlin?
The Soviet Union blocked West Berlin in an attempt to force the Western Allies out of the city and gain control over all of Berlin during the early stages of the Cold War.
-
How did the Berlin Airlift succeed?
The Berlin Airlift succeeded because the Western Allies, primarily the United States and Great Britain, managed to fly in enough supplies to sustain the entire population of West Berlin for nearly a year.
-
What was the outcome of the Berlin Blockade?
The blockade ended in May 1949 after the Soviets lifted the blockade, having failed to achieve their goal of forcing the Allies out of West Berlin.
-
What was the significance of the Berlin Airlift?
The Berlin Airlift became a symbol of Western resolve and solidarity during the Cold War and demonstrated the commitment of the Western Allies to protect Berlin.
- Luftbrücke: airlift
- versorgt: supplied
- Bürger: citizens
- unterbrach: blocked
- Verkehr: traffic
- Landwege: land routes
Question 177
Welche deutsche Stadt wurde nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg in vier Sektoren aufgeteilt?
- München
- Berlin
- Dresden
- Frankfurt/Oder
Question 177
Which German city was divided into four sectors after World War II?
- Munich
- Berlin
- Dresden
- Frankfurt/Oder
The correct answer is 'Berlin.' After World War II, Berlin was divided into four sectors, controlled by the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France.
-
Why was Berlin divided into four sectors after World War II?
Berlin was divided into four sectors controlled by the Allies (the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France) as part of the post-war occupation and administration of Germany.
-
Which countries controlled the four sectors of Berlin?
The four sectors of Berlin were controlled by the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France.
-
What was the significance of Berlin's division?
The division of Berlin symbolized the broader division of Germany and Europe during the Cold War, with East Berlin under Soviet control and West Berlin under Western Allied control.
-
How long did Berlin remain divided?
Berlin remained divided from the end of World War II in 1945 until the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, leading to the reunification of Germany in 1990.
-
What was life like in divided Berlin?
Life in divided Berlin was marked by political tension, with significant differences in living conditions between East Berlin (under communist control) and West Berlin (a democratic enclave).
- Sektoren: sectors
- Zweiter Weltkrieg: Second World War
- aufgeteilt: divided
Question 176
Wie waren die Besatzungszonen Deutschlands nach 1945 verteilt?
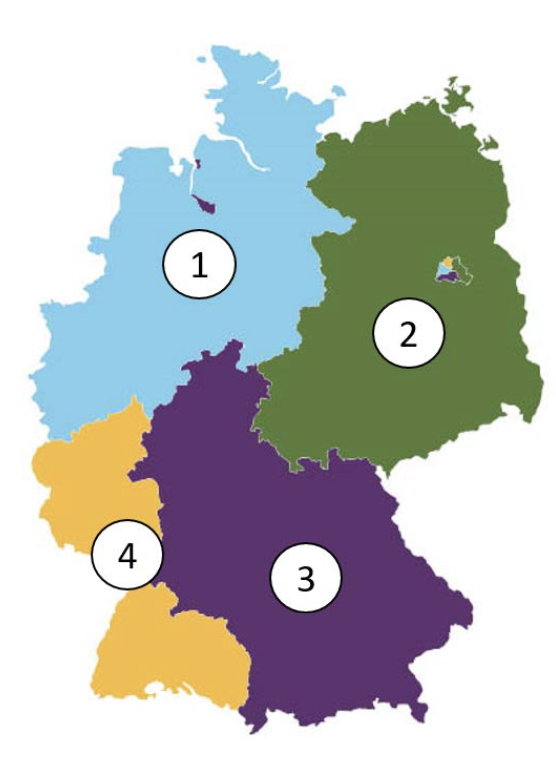
- 1=Großbritannien, 2=Sowjetunion, 3=Frankreich, 4=USA
- 1=Sowjetunion, 2=Großbritannien, 3=USA, 4=Frankreich
- 1=Großbritannien, 2=Sowjetunion, 3=USA, 4=Frankreich
- 1=Großbritannien, 2=USA, 3=Sowjetunion, 4=Frankreich
Question 176
How were Germany's occupation zones divided after 1945?

- 1=Great Britain, 2=Soviet Union, 3=France, 4=USA
- 1=Soviet Union, 2=Great Britain, 3=USA, 4=France
- 1=Great Britain, 2=Soviet Union, 3=USA, 4=France
- 1=Great Britain, 2=USA, 3=Soviet Union, 4=France
The correct answer is '1=Großbritannien, 2=Sowjetunion, 3=USA, 4=Frankreich.' (1=Great Britain, 2=Soviet Union, 3=USA, 4=France). After 1945, Germany was divided into four occupation zones controlled by the Allied powers: the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
How were Germany's occupation zones divided after 1945?
Germany was divided into four occupation zones controlled by the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France after World War II.
-
Which country controlled the eastern zone of Germany?
The eastern zone of Germany was controlled by the Soviet Union after World War II.
-
What was the purpose of the occupation zones in Germany?
The occupation zones were established to manage post-war Germany, with each of the Allied powers controlling and administering their respective zones.
-
When did the occupation zones in Germany end?
The occupation zones in Germany effectively ended with the formation of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) in 1949 and the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) under Soviet control.
- Besatzungszonen: occupation zones
- verteilten: divided
- Großbritannien: Great Britain
- Sowjetunion: Soviet Union
Question 175
Wie viele Besatzungszonen gab es in Deutschland nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg?
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Question 175
How many occupation zones were there in Germany after World War II?
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
The correct answer is '4.' After World War II, Germany was divided into four occupation zones, each controlled by one of the Allied powers: the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
How many occupation zones were there in Germany after World War II?
After World War II, Germany was divided into four occupation zones controlled by the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
Which countries controlled the four occupation zones?
The four occupation zones were controlled by the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
Why was Germany divided into occupation zones?
Germany was divided into occupation zones to allow the Allied powers to administer and control the country after its defeat in World War II.
-
Did the occupation zones include Berlin?
Yes, Berlin was also divided into four sectors, with each of the Allied powers controlling one sector.
- Besatzungszonen: occupation zones
- gab: were
- Zweiter Weltkrieg: Second World War
Question 174
Wann wurde die DDR gegründet?
- 1947
- 1949
- 1953
- 1956
Question 174
When was the DDR founded?
- 1947
- 1949
- 1953
- 1956
The correct answer is '1949.' The DDR (German Democratic Republic) was founded on October 7, 1949, as the communist state of East Germany under Soviet influence.
-
When was the DDR (German Democratic Republic) founded?
The DDR (German Democratic Republic) was founded on October 7, 1949.
-
Why was the DDR created?
The DDR was created as the eastern part of Germany under Soviet control, in response to the formation of West Germany (FRG) by the Western Allies. It became the communist state of East Germany.
-
What was the political system of the DDR?
The DDR had a socialist one-party political system under the control of the Socialist Unity Party (SED), closely aligned with the Soviet Union.
-
How long did the DDR exist?
The DDR existed from 1949 until its dissolution and reunification with West Germany in 1990.
-
What was life like in the DDR?
Life in the DDR was marked by strict government control, lack of personal freedoms, state-run industries, and a strong emphasis on communist ideology. The Stasi (state security service) also maintained extensive surveillance on the population.
- DDR: German Democratic Republic
- gegründet: founded
Question 173
Die Bundesrepublik Deutschland ist ein Gründungsmitglied …
- des Nordatlantikpakts (NATO).
- der Vereinten Nationen (VN).
- der Europäischen Union (EU).
- des Warschauer Pakts.
Question 173
The Federal Republic of Germany is a founding member of …
- of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
- of the United Nations (UN).
- of the European Union (EU).
- of the Warsaw Pact.
The correct answer is 'der Europäischen Union (EU).' Germany is a founding member of the European Union, which was established as the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1957 and later became the EU.
-
Is Germany a founding member of the European Union?
Yes, Germany is a founding member of the European Union. It helped establish the European Economic Community, which later became the EU.
-
When did Germany join NATO?
Germany joined NATO in 1955, but it is not a founding member of the organization.
-
What is the European Union (EU)?
The European Union is a political and economic union of 27 European countries, created to promote economic cooperation, free movement of goods, services, and people, as well as common policies on various issues.
-
Why was Germany not a founding member of the United Nations?
Germany was not a founding member of the United Nations because it was not allowed to join international organizations until after World War II due to its role in the conflict. Germany joined the UN in 1973.
-
What was the Warsaw Pact?
The Warsaw Pact was a military alliance of communist countries led by the Soviet Union, created in response to NATO. Germany was not a member of this alliance.
- Bundesrepublik: Federal Republic
- Gründungsmitglied: founding member
- Nordatlantikpakts: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Vereinten Nationen: United Nations
- Europäischen Union: European Union
- Warschauer Pakts: Warsaw Pact
Question 172
In welcher Besatzungszone wurde die DDR gegründet? In der …
- amerikanischen Besatzungszone
- französischen Besatzungszone
- britischen Besatzungszone
- sowjetischen Besatzungszone
Question 172
In which occupation zone was the DDR founded? In the …
- American occupation zone
- French occupation zone
- British occupation zone
- Soviet occupation zone
The correct answer is 'sowjetischen Besatzungszone' (Soviet occupation zone). The DDR (German Democratic Republic) was founded in the Soviet occupation zone in 1949.
-
In which occupation zone was the DDR founded?
The DDR (German Democratic Republic) was founded in the Soviet occupation zone in 1949.
-
Why was the DDR founded in the Soviet occupation zone?
The DDR was established in the Soviet occupation zone as a communist state under Soviet influence, in response to the formation of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) by the Western Allies.
-
What happened to the Soviet occupation zone?
The Soviet occupation zone became the German Democratic Republic (DDR), which existed from 1949 until the reunification of Germany in 1990.
-
How was Germany divided after World War II?
After World War II, Germany was divided into four occupation zones controlled by the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
What was the political system of the DDR?
The DDR had a socialist one-party political system, controlled by the Socialist Unity Party (SED) and closely aligned with the Soviet Union.
- Besatzungszone: occupation zone
- DDR: German Democratic Republic
- gegründet: founded
- sowjetisch: Soviet
Question 171
Soziale Marktwirtschaft bedeutet, die Wirtschaft …
- steuert sich allein nach Angebot und Nachfrage.
- wird vom Staat geplant und gesteuert, Angebot und Nachfrage werden nicht berücksichtigt.
- richtet sich nach der Nachfrage im Ausland.
- richtet sich nach Angebot und Nachfrage, aber der Staat sorgt für einen sozialen Ausgleich.
Question 171
Social market economy means the economy …
- is regulated solely by supply and demand.
- is planned and controlled by the state, with supply and demand not being considered.
- is oriented towards demand abroad.
- is guided by supply and demand, but the state ensures social balance.
The correct answer is 'richtet sich nach Angebot und Nachfrage, aber der Staat sorgt für einen sozialen Ausgleich' (is guided by supply and demand, but the state ensures social balance). The social market economy combines the principles of a free market with state intervention to promote social fairness.
-
What is the principle of social market economy?
The principle of the social market economy is to combine the efficiency of the free market with the need for social welfare. This means the economy is guided by supply and demand, but the state intervenes to ensure social equity.
-
How does the state influence the social market economy?
In a social market economy, the state intervenes to correct market failures and ensure that economic benefits are distributed more equally. This includes measures like social security systems and regulations to protect workers.
-
What is the difference between a social market economy and a planned economy?
A social market economy is guided by market forces of supply and demand, but the state ensures social balance. In contrast, a planned economy is centrally controlled and managed by the state, without relying on market mechanisms.
- Soziale Marktwirtschaft: social market economy
- Angebot: supply
- Nachfrage: demand
- sozialer Ausgleich: social balance
Question 170
Was gab es während der Zeit des Nationalsozialismus in Deutschland?
- das Verbot von Parteien
- das Recht zur freien Entfaltung der Persönlichkeit
- Pressefreiheit
- den Schutz der Menschenwürde
Question 170
What existed during the time of National Socialism in Germany?
- the ban on political parties
- the right to free personal development
- freedom of the press
- the protection of human dignity
The correct answer is 'das Verbot von Parteien' (the ban on political parties). During the National Socialist era in Germany, political freedoms were abolished, including the right to form opposition parties, and the government exercised strict control over all aspects of life.
-
What were some characteristics of the National Socialist regime in Germany?
The National Socialist regime in Germany was characterized by the banning of political parties, suppression of freedom of speech, control over the media, and widespread persecution of minorities.
-
What was the state of human rights during the Nazi era?
During the Nazi era, human rights were severely restricted, including the right to free speech, freedom of the press, and protection of human dignity.
-
Was there any opposition to the Nazi regime?
Yes, there were resistance movements and individual efforts to oppose the Nazi regime, but these were often met with brutal repression.
-
How did the National Socialist regime suppress political opposition?
The Nazi regime banned all political parties except for the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP) and violently suppressed any opposition to their rule.
- Nationalsozialismus: National Socialism
- Verbot: ban
- Parteien: political parties
- Pressefreiheit: freedom of the press
- Menschenwürde: human dignity
Question 169
Wann wurde die Bundesrepublik Deutschland gegründet?
- 1939
- 1945
- 1949
- 1951
Question 169
When was the Federal Republic of Germany founded?
- 1939
- 1945
- 1949
- 1951
The correct answer is '1949.' The Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland) was founded on May 23, 1949, after the division of Germany into East and West following World War II.
-
When was the Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland) founded?
The Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland) was founded on May 23, 1949.
-
Why was the Federal Republic of Germany founded in 1949?
The Federal Republic of Germany was founded in 1949 as the Western Allies sought to establish a democratic state in the western zones of occupation following World War II.
-
What was the political system of the newly founded Federal Republic of Germany?
The Federal Republic of Germany was established as a democratic, federal state with a parliamentary system of government.
-
What was the significance of the Federal Republic of Germany's founding in relation to East Germany?
The founding of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) in 1949 was paralleled by the establishment of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) in the Soviet occupation zone, leading to the division of Germany until reunification in 1990.
- gegründet: founded
- Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Federal Republic of Germany
Question 168
Welches Land war keine "Alliierte Besatzungsmacht" in Deutschland?
- USA
- Sowjetunion
- Frankreich
- Japan
Question 168
Which country was not an 'Allied occupying power' in Germany?
- USA
- Soviet Union
- France
- Japan
The correct answer is 'Japan.' The Allied occupation powers in Germany after World War II were the USA, the Soviet Union, France, and Great Britain. Japan was not an occupying power in Germany.
-
Which countries were the Allied occupation powers in Germany after World War II?
The Allied occupation powers in Germany after World War II were the USA, Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
Why was Japan not an occupying power in Germany?
Japan was not an occupying power in Germany because it was itself one of the Axis powers defeated in World War II and was occupied by the Allies after the war.
-
What was the role of the Allied occupation powers in Germany?
The Allied occupation powers controlled Germany after its defeat in World War II, dividing the country into four zones of occupation to administer and oversee its rebuilding.
-
How long did the Allied occupation of Germany last?
The Allied occupation of Germany lasted until 1949 in the west with the formation of the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, and technically until 1990 when Germany was officially reunified.
- Alliierte: Allied
- Besatzungsmacht: occupying power
- Sowjetunion: Soviet Union
Question 167
Welche Länder wurden nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg in Deutschland als "Alliierte Besatzungsmächte" bezeichnet?
- Sowjetunion, Großbritannien, Polen, Schweden
- Frankreich, Sowjetunion, Italien, Japan
- USA, Sowjetunion, Spanien, Portugal
- USA, Sowjetunion, Großbritannien, Frankreich
Question 167
Which countries were referred to as 'Allied occupation powers' in Germany after World War II?
- Soviet Union, Great Britain, Poland, Sweden
- France, Soviet Union, Italy, Japan
- USA, Soviet Union, Spain, Portugal
- USA, Soviet Union, Great Britain, France
The correct answer is 'USA, Sowjetunion, Großbritannien, Frankreich' (USA, Soviet Union, Great Britain, France). These four countries were the Allied occupation powers in Germany after World War II.
-
Which countries were the Allied occupation powers in Germany after World War II?
The Allied occupation powers in Germany after World War II were the USA, Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
Why were these four countries chosen as the occupying powers?
These four countries were chosen as the occupying powers because they were the main Allied forces that defeated Nazi Germany in World War II.
-
How was Germany divided among the Allied occupation powers?
Germany was divided into four zones of occupation, each controlled by one of the Allied powers: the USA, Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France.
-
Did any other countries occupy parts of Germany?
No, only the USA, Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France occupied parts of Germany as the official Allied occupation powers.
- Alliierte: Allied
- Besatzungsmächte: occupying powers
- Sowjetunion: Soviet Union
- Großbritannien: Great Britain
- Frankreich: France
Question 166
Bei welchen Demonstrationen in Deutschland riefen die Menschen "Wir sind das Volk"?
- beim Arbeiteraufstand 1953 in der DDR
- bei den Demonstrationen 1968 in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland
- bei den Anti-Atomkraft-Demonstrationen 1985 in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland
- bei den Montagsdemonstrationen 1989 in der DDR
Question 166
At which demonstrations in Germany did people chant 'We are the people'?
- during the workers' uprising in 1953 in the DDR
- during the 1968 demonstrations in the Federal Republic of Germany
- during the 1985 anti-nuclear power demonstrations in the Federal Republic of Germany
- during the Monday demonstrations in 1989 in the DDR
The correct answer is 'bei den Montagsdemonstrationen 1989 in der DDR' (during the Monday demonstrations in 1989 in the DDR). The slogan 'Wir sind das Volk' was famously used during the peaceful protests against the East German government that led to the fall of the Berlin Wall.
-
When were the Monday demonstrations in East Germany?
The Monday demonstrations took place in 1989 in East Germany (DDR) as part of the peaceful protests that led to the fall of the Berlin Wall.
-
What was the significance of the slogan 'Wir sind das Volk'?
'Wir sind das Volk' (We are the people) was a slogan used during the 1989 Monday demonstrations in the DDR to demand democratic reforms and express popular opposition to the East German government.
-
How did the Monday demonstrations contribute to the fall of the Berlin Wall?
The Monday demonstrations played a crucial role in building public pressure against the East German regime, leading to increased demands for freedom, democracy, and eventually the opening of the Berlin Wall.
-
Why were the Monday demonstrations important in German history?
The Monday demonstrations were a key part of the peaceful revolution in East Germany, which contributed to the reunification of Germany and the end of the Cold War.
- Demonstrationen: demonstrations
- Volk: people
- Montagsdemonstrationen: Monday demonstrations
- DDR: German Democratic Republic